The EE enzyme and DNA repair in cancer tumors
Cells have a number of options available to them following DNA damage, including induction of apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and DNA repair. Subsequently, cancer cells often overexpress DNA repair proteins, which promote cell survival and therefore negatively affect treatment efficacy and development of resistance. Several studies suggest that targeting DNA repair endonucleases in combination with DNA-damaging agents may be a promising anticancer strategy.
In a study conducted by Chow et al, the endo-exonuclease was overexpressed in a variety of cancer cells and was proposed as an effective target for developing anticancer drugs. The authors identified pentamidine, an inhibitor of the endo-exonuclease as determined by enzyme kinetic assay. Pentamidine was shown to possess the ability to selectively kill cancer cells. The LD50 of pentamidine on cancer cells maintained in vitro was correlated with the EE enzyme activity. Tumor cell that has been treated with pentamidine is reduced in the endo-exonuclease group compared to the untreated control.
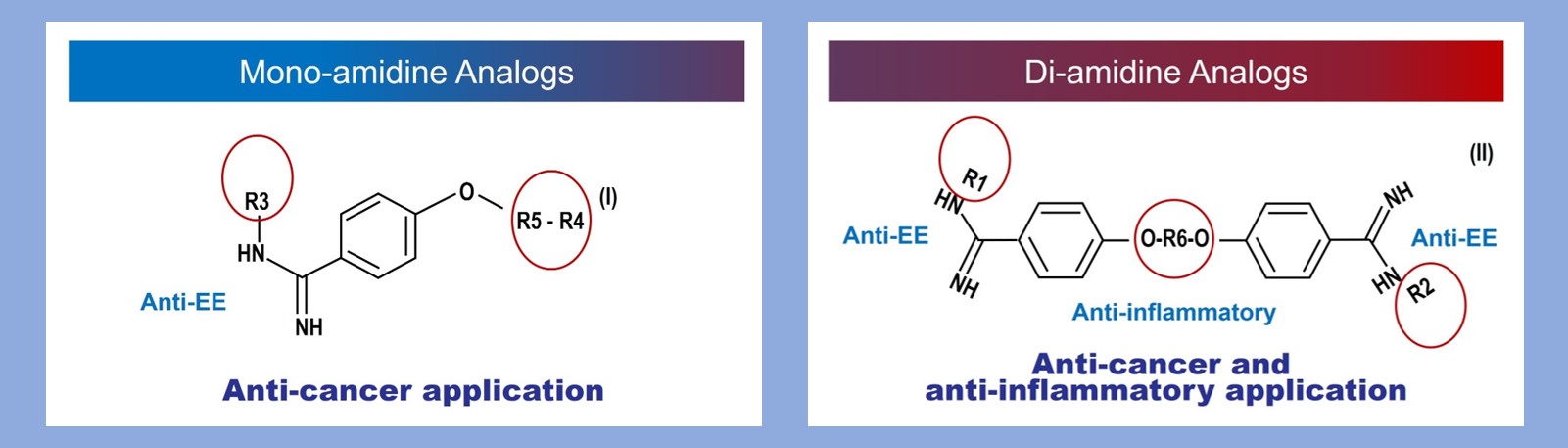
Montdorex analogs for anti-cancer therapy
We have screened multiple amidine analogs, displaying various length of the backbone molecules as well as molecular end modification of pentamidine. It has been shown that the ends of the molecule are the active moiety for both cytotoxicity and nuclease inhibition. The following illustration displays two types of analogs that Montdorex is pursuing. In vitro studies have shown that pentamidine analogs have enhanced endo-exonuclease inhibition and cytotoxicity.
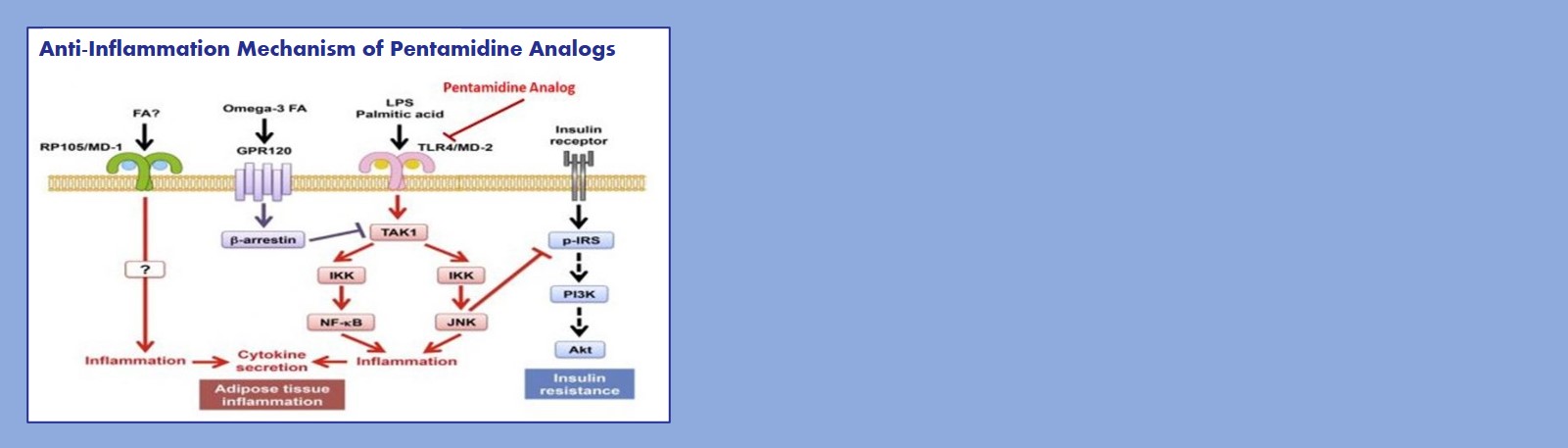
Anti-inflammation application of pentamidine and its analogs
The effect of pentamidine in the inflammation process and binding to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is well documented. The beneficial effect of pentamidine as an anti-inflammatory agent is demonstrated by its ability to improve experimentally induced acute colitis and to block hepatotoxic injury in mice models.
Furthermore, oral formulation of pentamidine is highly hepatoselective and hepatoprotective, which makes this class of compounds particularly promising for potential treatment of chronic GI and liver diseases. Montdorex has identified lead pentamidine analogs that do not inhibit the EE enzyme (non cytotoxic analogs) for anti-inflammation development.